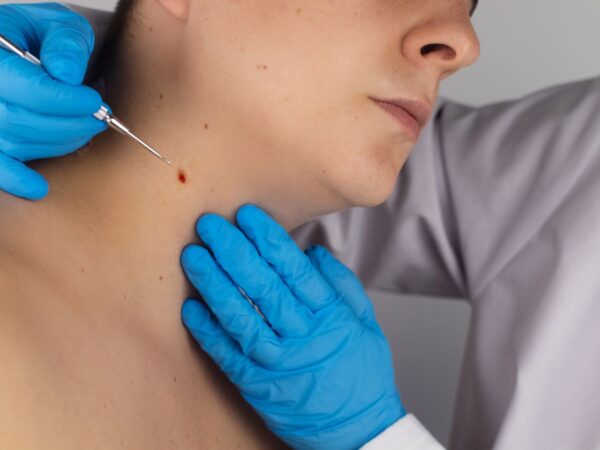
Papillomas - What are they?
Papillomas are benign skin growths. Colloquially, they are also called "moles", but they have nothing to do with the "olives" of the skin (skin moles). They are small, round, with sessile or stalked appendages of the epidermis. Their surface is smooth or warty (like cauliflower). Papillomas are usually skin-colored but can be tan or even dark brown.
Papillomas – Etiology
Most people in both sexes have papillomas after the age of 25-30 with about 60% of people developing them by the age of 70. Because everyone's immune system is different, some people get infected more easily than others. The incubation time between skin contact and the appearance of the papilloma can be up to three months.
Papillomas are caused by HPV (Human Papilloma Virus), the viruses that cause warts and warts. However, papillomas are not equally contagious. That is, they are not easily transmitted from person to person. Papillomas can multiply and spread in the same person after rubbing or trauma to the area. The main responsible HPV viruses that cause papillomas they are HPV 6 and HPV 11. These are essentially low-risk viruses.
Papillomas are caused by HPV (Human Papilloma Virus), the viruses that cause warts and warts. However, papillomas are not equally contagious. That is, they are not easily transmitted from person to person. Papillomas can multiply and spread in the same person after rubbing or trauma to the area. The main responsible HPV viruses that cause papillomas they are HPV 6 and HPV 11. These are essentially low-risk viruses.
Before & After Treatment
You can see the course of each treatment in the slider below. By pressing the arrows at the bottom you can see the result per session

First session
At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti.

Second session
At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti.
Third session
At vero eos et accusamus et iusto odio dignissimos ducimus qui blanditiis praesentium voluptatum deleniti atque corrupti.
Papillomas – Symptomatology
Papillomas are usually asymptomatic, i.e. they do not cause discomfort. They usually appear in warm and moist areas of the body, where the skin creates folds (on the face and especially on the eyelids, neck, armpits, inguinal folds, under the breast, etc.) and favors the growth of HPV viruses due to the increased skin friction with skin.
But often as they grow or multiply they can cause various discomforts. Discomfort also occurs in case of twisting of their stem, in which case inflammation is created which causes sensitivity. Some patients with papillomas report itching in the area and a burning sensation, especially in the summer months in conditions of intense sweating. Many times the papillae are injured and bleed causing worry to the patients. Scratching or rubbing (eg constant irritation from underwear-bra) can lead to inflammation of the papillae with swelling and pain.
Sometimes the papillae become very large and form the acrochordons or hanging terminus.
Papillomas can occur in practically everyone. But there are some predisposing factors and their appearance is favored in certain groups of people.
It has been observed that papillomas appear more commonly in people who are overweight or obese. Possibly due to increased sweating and creation of folds (which lead to increased skin-to-skin friction) in the skin that favor the growth of human papillomaviruses. In these cases, losing weight also reduces the appearance of new papillomas.
Papillomas often first appear or multiply during pregnancy and especially in the second half. They are found more often in the lateral cervical region (neck), in the armpits and under the chest. Both weight gain and hormonal factors probably play a role in this. Another cause may be the decline of the immune system during pregnancy. It is also common for pre-existing papillomas to increase in size during pregnancy for the same reasons. This should not worry pregnant women. It is good to treat papillomas after childbirth. In the event that papillomas appear in the breast area near the nipple, the laser treatment can be done immediately after delivery so that breastfeeding can follow safely. Many times there is an automatic subversion (recession) of the papillae after childbirth. In the event that this does not happen, we plan their removal, preferably with a laser.
Papillomas often occur in diabetics. In these cases, they should be treated immediately, as the risk of papilloma inflammation is greater in diabetics.
Trauma favors the spread of papillomas. Even mild injury such as scrubbing with a sponge while bathing, as well as with towels, multiplies the papillomas. The same applies to chains around the neck which, by friction, aggravate the problem of cervical papillomas. Even more, shaving the area affected by papillomas favors the transmission of the virus, as the razor carries the virus to new areas where it inoculates (enters the skin).
Papillomas are caused by the same group of viruses that cause warts and warts. Therefore papilloma and wart or wart often coexist in many patients.
There is no hereditary predisposition to the appearance of papillomas, as it is a condition caused by a skin virus. Nevertheless it seems that when a person suffers from papillomas and other people in his family probably display them.
The following measures prevent the appearance of papillomas
- No scrubbing with a sponge or towels after bathing if papillomas are present
- Avoid using chains and necklaces around the neck if there are papillomas in the cervical region
- We avoid touching the papillae with our hands
- Avoid shaving the affected area papillomas
We avoid using on healthy areas of the body razors and nail clippers that have been used on areas with papillomas - Weight reduction in case of obesity.
- Immediate destruction and removal of papillomas with laser as soon as their existence is established.
- Vaccination against HPV viruses with the multivalent vaccine reduces the risk of papillomas, as it protects against HPV 6,11,16,18.